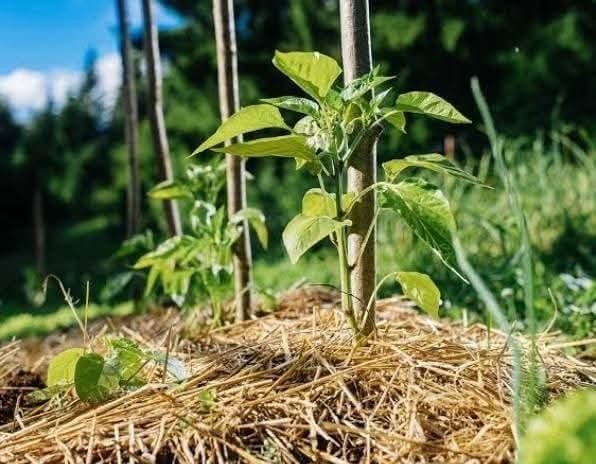
MULCHING 🌾
Mulching is the practice of covering the soil surface around plants with a layer of material, either organic straw, leaves, grass clippings, or compost) or inorganic (e.g., plastic sheets, gravel, or stones). It serves as a protective layer that improves soil conditions and supports plant growth.
BENEFITS AND ADVANTAGES OF MULCHING:-
1. Moisture Retention: Mulch reduces water evaporation from the soil, keeping it moist for longer periods, which minimizes the need for frequent watering.
2. Temperature Regulation: Mulch acts as an insulating layer, protecting roots from extreme temperatures. It keeps the soil cooler in hot weather and warmer in cold weather.
3. Weed Suppression: By blocking sunlight, mulch inhibits the growth of weeds, reducing competition for nutrients and water.
4. Soil Erosion Prevention: Mulch reduces the impact of heavy rains on the soil, preventing erosion and maintaining soil structure.
5. Improved Soil Fertility (for organic mulch): As organic mulch decomposes, it adds nutrients to the soil, improving its fertility and structure.
6. Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal: Mulch gives gardens and landscapes a clean and uniform appearance, enhancing visual appeal.
7. Pest Control: Certain types of mulch, like cedar or pine bark, can deter pests due to their natural oils and scent.
8. Reduction of Soil Compaction: Mulch minimizes the compaction of soil caused by rain and foot traffic, promoting better root development.
9. Improved Root Health: By maintaining consistent soil moisture and temperature, mulch creates a favorable environment for healthy root growth.
10. Environmentally Friendly: Organic mulch recycles natural materials, reducing waste and promoting sustainable gardening practices.
COMMON MATERIALS FOR MULCHING :-
1. Organic Mulch: Straw, grass clippings, wood chips, bark, leaves, compost, or sawdust.
2. Inorganic Mulch: Plastic sheets, stones, gravel, or rubber mulch.
PROCEDURE :-
1. Prepare the Soil: Remove weeds and grass. Loosen the soil for better aeration. Water the soil to ensure it’s moist.
2. Choose Mulch Material: Select organic (e.g., straw, leaves) or inorganic (e.g., stones, plastic) mulch based on your needs.
3. Apply Mulch: Spread evenly around plants, leaving space around stems. Apply 2-4 inches thick, depending on the material.
4. Maintain the Mulch: Inspect for compaction or decomposition. Replenish as needed to maintain thickness.
5. Monitor Plant Health: Adjust mulch if plants show signs of overwatering or poor drainage. This ensures effective mulching for plant growth and soil health.